How to Play Backgammon
A Complete Guide to the Rules & Strategy
Introduction
Backgammon is one of the oldest board games in the world — dating back over 5,000 years. Simple to learn yet tough to master. It blends strategy, luck, and timing in a race to bear off your checkers before your opponent.
This guide will walk you through the basic backgammon rules — from setup to winning — so you can start playing confidently in minutes.
If you would rather watch a beginner backgammon video, check out our new series on beginner backgammon strategy, or start with the Ultra Fast Guide video below.
Backgammon Rules: A Quick Summary
Board Layout
Backgammon is a board game for two players.
Each player has
2 dice
15 checkers
There’s 1 doubling cube.
The board is divided into 4 quadrants: Two outfields and two homes. Each quadrant is divided into 6 points (the triangular shapes) making a total of 24 points.
The vertical divider is called “the bar” and the bear-off trays are located on the side of the board.
How to Set Up the Board
White has:
Two checkers on 24 (backmost checkers)
Five checkers on 13 (midpoint)
Three checkers on 8
Five checkers on 6
Black’s checkers are placed opposite of White’s.
White moves counter-clockwise and Black moves clockwise.
How to Win
The objective of Backgammon is to move all your checkers into your home board, and then take them off (We explain this later on). It’s only possible to take off checkers while all of your checkers are inside your home board. The first player to take off all their checkers wins the game.
Starting the Game
The players start the game by rolling one dice each - this is called the “opening roll”. If the same number is rolled in the opening, both players must make a re-roll.
The player who rolls the highest number wins the opening roll and must play the rolled dice combination. For the remaining turns of the game, each player rolls two dice.
Here the bottom White player won the opening roll by rolling a 3 which is higher than Blacks roll of 1. White picks up his dice and Black now rolls his dice to start the 2nd roll of the game.
Doubles & Moving Checkers
When a player rolls two identical numbers it’s called “to roll a double”. Rolling a double will give you twice the numbers. Example: If you roll two 2’s you now have four 2’s you can move. This goes for any double that you roll.
For any type of roll, you have to use both dice numbers if they can both be used! You can decide whether to combine the dice numbers and move a single checker, or to separate the dice numbers and move two individual checkers - or in the case of a double roll, move up to four individual checkers.
There’s no limit to how many checkers you can place on a point.
Your turn ends when you’ve moved your checkers and you pick up the dice. It is allowed to try out various move combinations. The move is only confirmed once you pick up the dice.
Advanced Backgammon Strategy: How to Win More Matches
There’s more to backgammon than the basic rules. Read on to learn more backgammon tips, strategies and advanced concepts to help you win.
Anchors & Primes
Two or more checkers on a point is called an anchor or point. Your opponent’s checkers can’t move to your anchors as you are occupying these points. When anchors are placed next to each other it’s called a prime. To get past your opponent’s prime or anchor, your checkers must be able to land on a free point.
Flexibility & Efficiency
Your probability of making anchors is much higher if you play according to the concept of flexibility.
When you play with flexibility you place your checkers, not in stacks, but distributed on several points. This increases the chance to make anchors.
There’s a high risk of getting hit, but often the benefit is higher than the risk!
In position 1 the move leaves us inflexible, when stacking checkers. In position 2 we distribute checkers for more flexibility.
Efficiency
The concept of efficiency is closely linked to flexibility. As backgammon legend Paul Magriel said: “Put your checkers where they belong”.
The core value of this quote is that each checker should do something productive. Each move matters. To illustrate the concept briefly check out these two highly contrasting positions:
In the first position here we see that White has 10 checkers forming a strong prime. All of those checkers are doing something highly valuable.
In the second position, White has horrible effiency with a dead checker on the 1-point, and two additional checkers that are never going to be able to add prime value.
Hitting Checkers
A single checker can be “hit” if your opponent’s checker lands on it. When a checker is hit it must be placed on the bar. When a player has checkers on the bar, they must use their roll to enter the checkers into their opponent’s home board before moving any other checkers.
A checker is entered by moving it to any point in your opponent’s home board that is not blocked by an anchor. If both your dice numbers are blocked by your opponent’s anchors, you must stay on the bar and your turn ends.
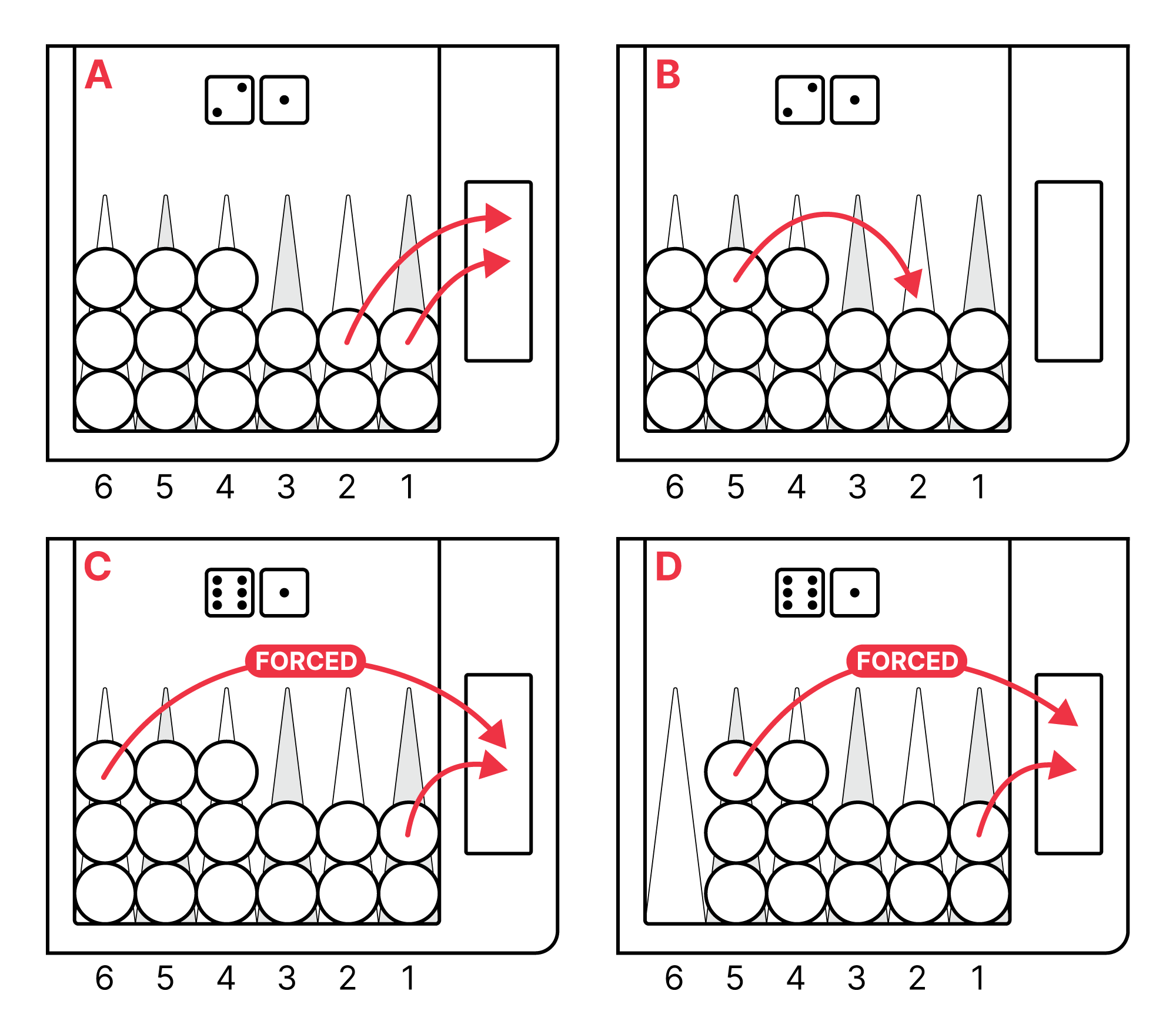
Forced Moves
If it is possible to use both dice, you must do so. You cannot make a move that prevents you from playing the second dice if there is a move that allows both dice to be played (A).
In a bear-off situation, you are not required to move the higher dice first. You may play the lower dice first, which may then result in a forced move with the higher dice (B). If you can only use one of the two dice, you must always play the dice with the higher number.
Taking Off Checkers
When all of your checkers are inside your home board, you can now move them out of the board (A). You are free to make any legal moves in your home board with the given dice numbers, including not taking off checkers (B).
If you roll a number higher than the point you have checkers on (D), you must take off checkers from the backmost point containing checkers.
Strategies
Backgammon has 4 basic strategies.
Mastering when and how to use them is what makes the game both complex and thrilling — it’s a skill that takes a lifetime to perfect. If you’re playing against someone who doesn’t understand these strategies, you’ll have a major edge.
One key factor determines which strategy to use: the race — your pip count.
When you're behind in the race, you’ll usually choose priming or contact.
When you're ahead, blitzing or racing is often the best approach.
1. Prime: Building a wall of anchors from which your opponent’s backmost checkers can’t escape.
Priming is a powerful strategy, even when you build just a 4-point prime. It’s typically used when you’ve had some fortunate early rolls that let you connect points, and when you're not too far ahead in the race. If you’re ahead, a prime loses value — you’ll likely have to break it before your opponent is truly trapped.
Curious about this strategy? Read about prime vs. primes positions here
2. Blitz: You overpower your opponent by hitting and closing out your home board with anchors so that they can’t enter from the bar.
Blitzing typically happens early in the game, and its success depends on having enough “men in the zone” — checkers positioned in your home board and outer quadrant. These checkers are needed to follow up on hits and close points.
As a rule of thumb: 8 checkers is weak, 9 is acceptable, and 10–11 is strong. Blitzing is usually only effective when you're ahead in the race, meaning your pip count is lower than your opponent’s.
More about blitzing here.
3. Race: Simply bet on getting higher dice rolls than your opponent, so you can be the first player to take off all your checkers.
Lucky to escape your backmost checkers to the 13-point (midpoint) in the early game? Then you might consider going strictly for a race. Avoid getting hit and leaving direct shots. But be careful, if your position becomes too stiff with no flexiblity to place checkers you will have difficulty playing against your opponent’s anchors.
4. Contact or “Holding Game”: When behind in the race sit tight by having an anchor in your opponent’s home territory from which you wait for a chance to hit.
When playing backgammon you will be playing a lot of contact games as this is the most common strategy for the player behind in the race.
If you’ve secured an anchor in your opponent’s home board, you always have a fighting chance to turn the game around!
If you are very far behind in the race (at least 70 pips), you can even have two innerboard anchors in place while you build your homeboard. This contact strategy variant is called having a “backgame”.
Point System
There are three ways of winning a game of backgammon:
Single (1 point): When you have taken off all your checkers and your opponent has taken off between 1 and 14 checkers.
Gammon (2 points): When you have taken off all your checkers and your opponent hasn’t taken off any checkers.
Backgammon (3 points): When you have taken off all of your checkers and your opponent hasn’t taken off any checkers and still has 1 or more checkers either on the bar OR inside your home board.
Doubling Cube
When you have an advantage in the game you usually want to double your opponent. The cube must be offered when it's your turn and before rolling the dice.
The points won in the game are multiplied by the level of the doubling cube. When the cube is first offered and taken the level is raised from 1 to 2, the levels can only double up one step at a time.
Winning a single game with the cube level on 2 will give you 2 points, winning a gammon (which is 2 points) with a cube level of 4 will give you 8 points.
The doubling cube has side 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 (here replaced by a logo).
Black doubles White, and White now has two options: Take or Pass
If he passes the game ends and his opponent wins the number of points of the cube level. Passing an initial cube wins the opponent 1 point, passing a redouble from 2 to 4 wins the opponent 2 points, and so on and so forth.
White takes, thereby becoming the owner of the cube, and will be the only one who can offer the next double from now on.
The game continues and both players now play on for the new higher stakes and Black now makes her roll.
Pip Counting
Backgammon is fundamentally a race to see who can move all their checkers to the finish line first. The “pip count” is a way to measure who’s ahead in that race.
The player with the lower pip count is leading. Your pip count helps determine the best strategy to use in any given position:
If you're ahead, you’ll want to avoid getting hit and focus on safely bringing your checkers into your home board and take them off.
If you're behind, your best chance is to hit an opposing checker — because playing a pure race when you’re behind in the race, will likely result in a loss. You could be lucky, but don’t rely on luck. Rely on skill!
In the opening both players have 167 pips each. And when the players start rolling dice and hitting checkers the pip count changes. Keeping track of the pip count in exact numbers is something advanced players can do some what easily. But for new players it is easier to look at the big picture and guage who is ahead and who is behind - often it is quite obvious.
Game Formats
In backgammon, two primary formats are commonly played: money games and match play.
Money Games
In this format, each game is independent, and players can decide to play for stakes, though playing for actual money is optional. Games continue indefinitely, with players agreeing when to stop, typically when one decides to conclude the session.
Jacoby Rule
A noteworthy detail: in money games the jacoby rule applies meaning you can only win a gammon if atleast one double has taken place in the game.
Match Play
This format is standard in tournaments, where players compete to reach a predetermined point total to win the match.
Common match lengths include 1, 3, 5, or 7 points, with major tournaments often featuring matches of 17 points or more.
Crawford Rule
The doubling cube is used, and the Crawford Rule applies when a player is one point away from winning, restricting the use of the doubling cube for one game to balance the advantage.
| Match Play | Money Games | |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 1–25 (typically) | Infinite |
| Crawford Rule | Yes | No |
| Jacoby Rule | No | Yes |
| Use case | Tournaments | Gambling |